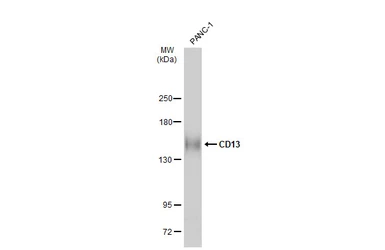
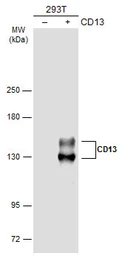
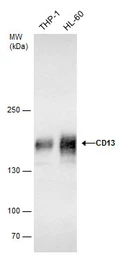
CD13 antibody
Cat. No. GTX102788
Cat. No. GTX102788
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
ApplicationsWB IHC-P
-
ReactivityHuman