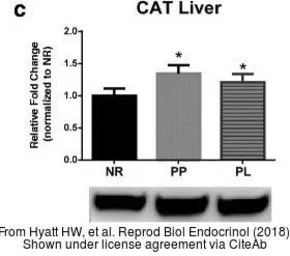
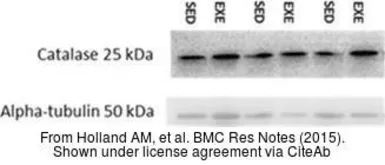
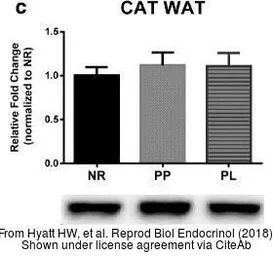
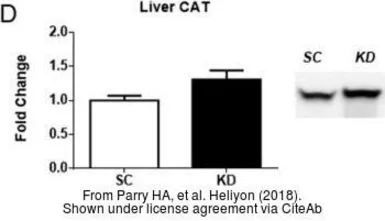
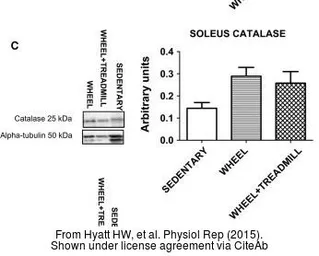
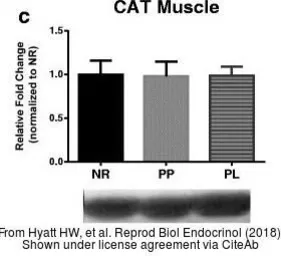
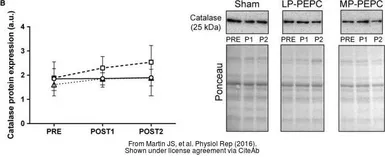
Catalase antibody
Cat. No. GTX110704
Cat. No. GTX110704
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
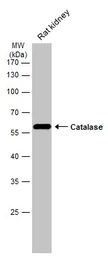
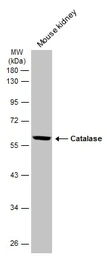
ApplicationsWB IHC-P IHC-Fr
-
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
Summary
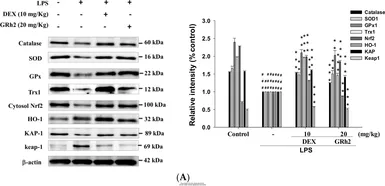
Catalase antibody detects catalase protein, an antioxidant enzyme (predicted molecular weight of 60 kDa). Mutation of the CAT gene that codes for catalase protein can result in acatalasemia. This catalase antibody (GTX110704) is a well-known reagent cited in multiple publications.