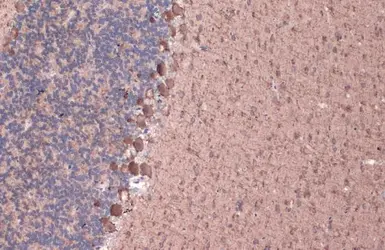
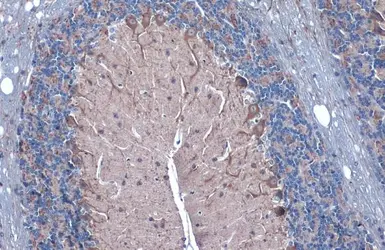
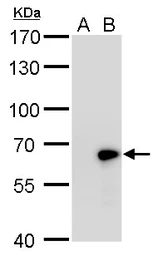
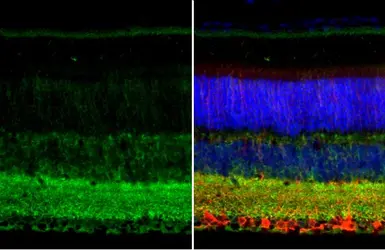
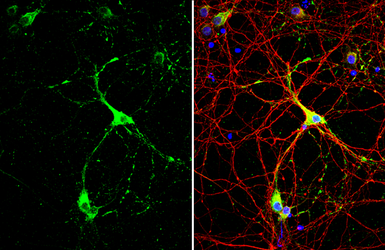
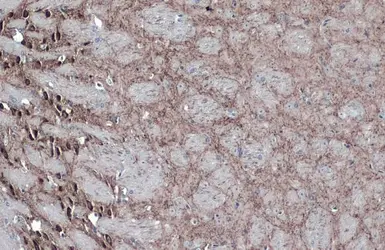
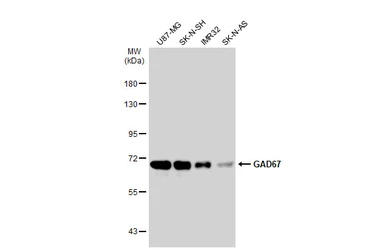
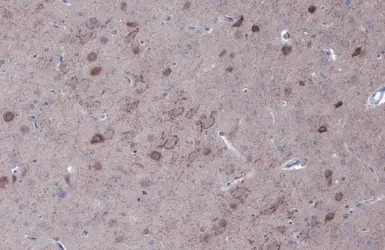
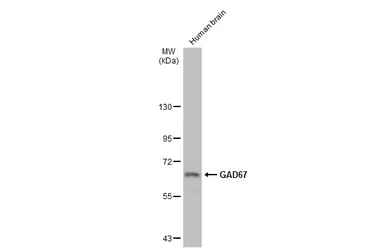
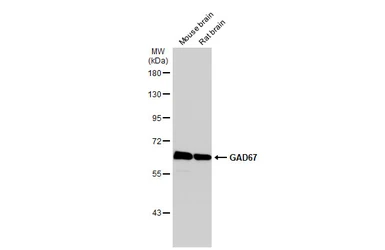
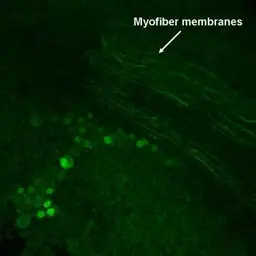
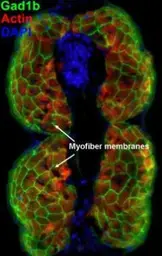
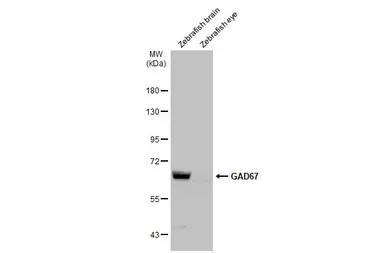
GAD67 antibody
Cat. No. GTX101881
Cat. No. GTX101881
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
ApplicationsWB ICC/IF IHC-P IHC-Fr IHC-Wm IHC IHC (Free Floating)
-
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish, Monkey