IL1 beta antibody
Cat. No. GTX22105
Cat. No. GTX22105
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
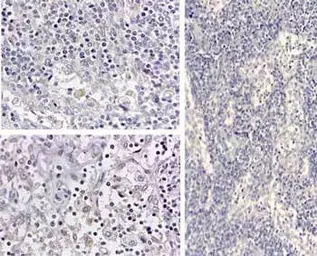
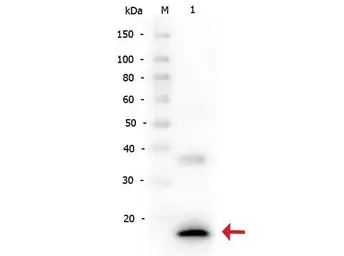
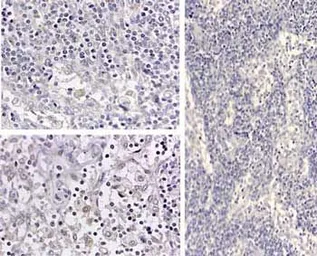
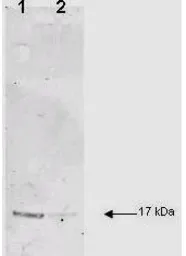
ApplicationsWB IHC-P IHC-Fr FCM IP ELISA Neutralizing /Inhibition
-
ReactivityHuman, Dog