LDL Receptor antibody, Internal
Cat. No. GTX80914
Cat. No. GTX80914
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
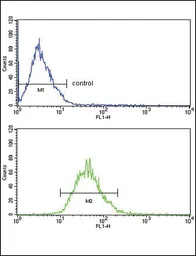
ApplicationsWB FCM
-
ReactivityHuman, Mouse