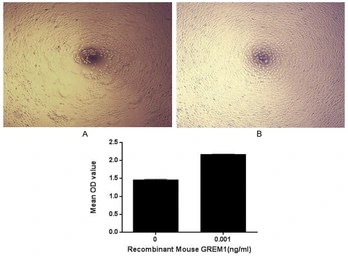
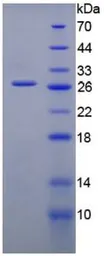
Mouse Gremlin 1 protein, His tag (active)
Cat. No. GTX00318-pro
Cat. No. GTX00318-pro
-
ApplicationsFunctional Assay
-
SpeciesMouse