PPAR alpha antibody
Cat. No. GTX101098
Cat. No. GTX101098
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
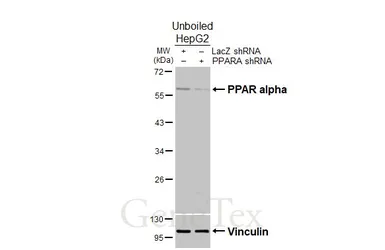
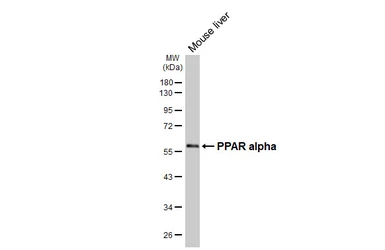
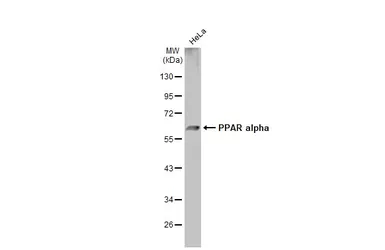
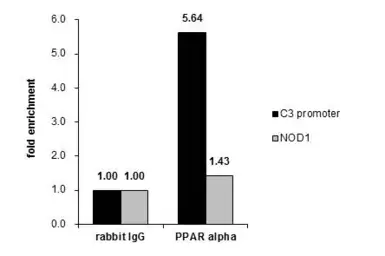
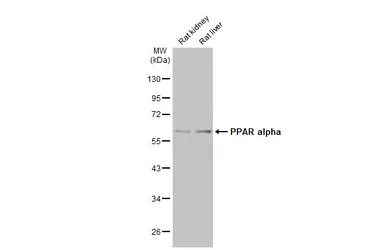
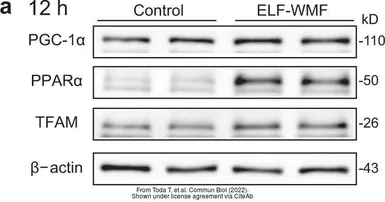
ApplicationsWB IHC-P IP ChIP assay
-
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat, Honeybee, Queen Bee, Plant