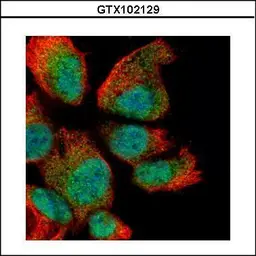
RAN antibody
Cat. No. GTX102129
Cat. No. GTX102129
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
ApplicationsICC/IF
-
ReactivityHuman