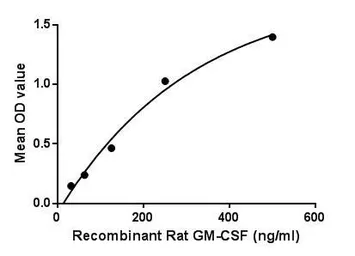
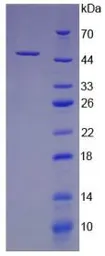
Rat GM-CSF protein, His tag
Cat. No. GTX00365-pro
Cat. No. GTX00365-pro
-
ApplicationsFunctional Assay
-
SpeciesRat