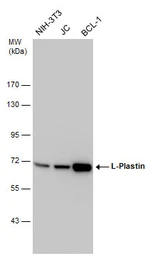
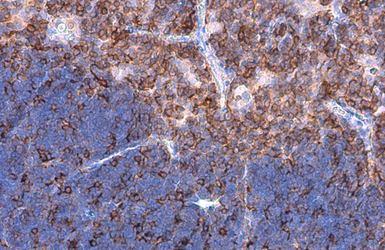
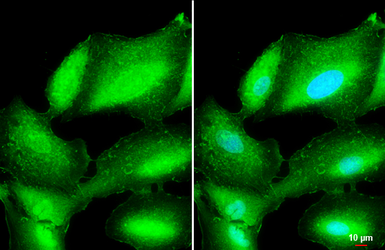
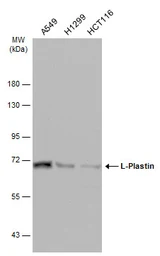
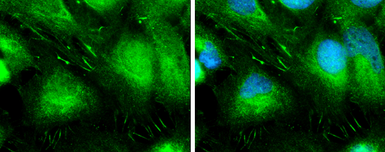
L-Plastin antibody
Cat. No. GTX105789
Cat. No. GTX105789
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
ApplicationsWB ICC/IF IHC-P IHC-Fr
-
ReactivityHuman, Mouse