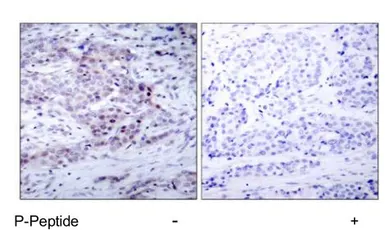
NFkB p100 (phospho Ser869) antibody
Cat. No. GTX79001
Cat. No. GTX79001
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
ApplicationsWB IHC-P
-
ReactivityHuman