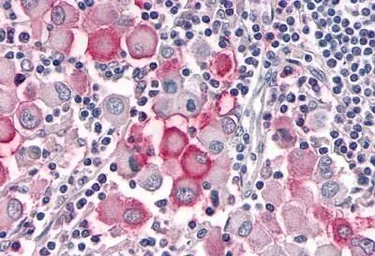
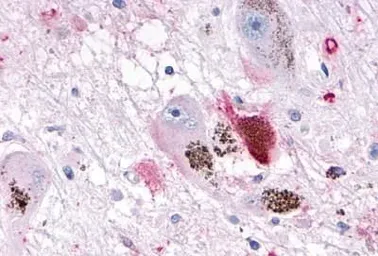
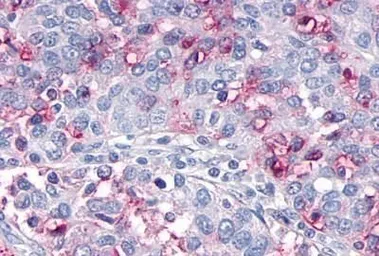
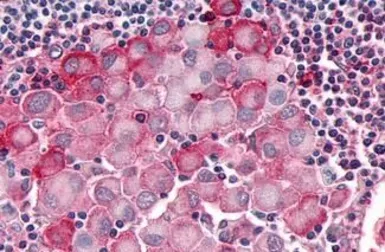
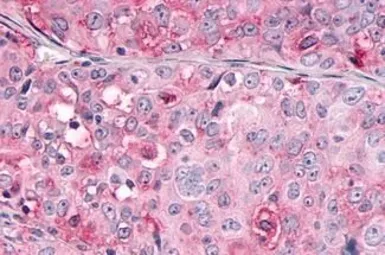
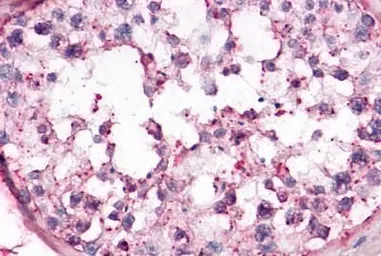
OR10R2 antibody
Cat. No. GTX71527
Cat. No. GTX71527
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
ApplicationsIHC-P
-
ReactivityHuman, Rabbit, Bovine, Monkey