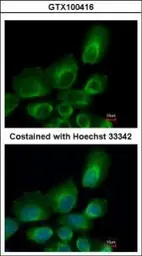
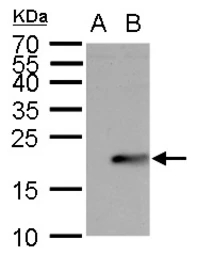
UBE2B antibody
Cat. No. GTX100416
Cat. No. GTX100416
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
ApplicationsWB ICC/IF
-
ReactivityHuman, Mouse