XRCC4 antibody
Cat. No. GTX109632
Cat. No. GTX109632
-
HostRabbit
-
ClonalityPolyclonal
-
IsotypeIgG
-
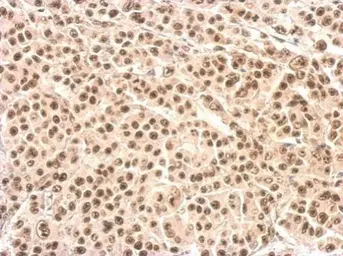
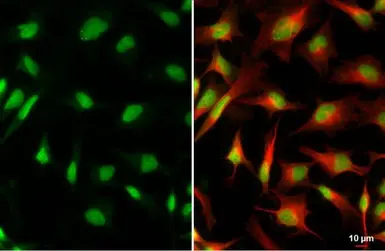
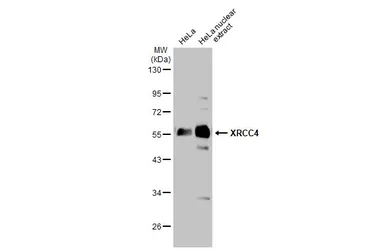
ApplicationsWB ICC/IF IHC-P
-
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
Summary
XRCC4 antibody detects X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 4 (XRCC4; predicted molecular weight ~38 kDa), a crucial component of the canonical non-homologous end-joining pathway to repair DNA double-strand breaks. The protein functions by stabilizing and activating DNA Ligase IV, as well as bridging the DNA ends. Mutations or disruption of XRCC4 have been linked to a large number of cancers as well as to a form of dwarfism.